What is a black hole?
A black hole is (to put it in a short and easy way) An incredible amount of mass squished in to a tiny dot, this enormous amount of mass then resolves in a strong gravitational pull that not even light can escape from. (Now for the complicated explanation) A black hole is a giant supernova that has exploded at the end of it's lifespan and all of the mass colapsed in to the center. As some of you might alredy know the gravitational pull of a planet is in proportions with it's mass, and because this enormous mass that once was a giant supernova has been pushed in to a tiny dot the gravitational pull is so incredible that not even light can escape it. (that is why it is called a black hole, because the light cant return from the center and therefore it apears black in a telescope.)
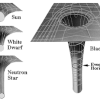
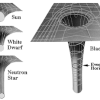
All stars bend the space and time arround them, this is explaned with the picture above, the grater the mass the more it bends the space and time arround it. As you see there, a Sun bends the space a little bit, a White Dwarf (an exploded sun) bends the space a little more due to the same mass in a smaller package. A Neutron Star is the same mass but an even smaller volume. The Black Hole is the most mass in the smallest package and therefore it bends the time so much it stops and space so much nothing can escape. If you were to go into a black hole, at first the time around you would slow down but you would not notice it, the gravity would be pulling you in and you would feel like you were very heavy. After entering the Event Horizon the difference between the gravity at your feet and at your head would be so incredible that it would start stretching you out like a spaghetti, eventually your body would dissolve into its atoms and you would be pressed into the singularity at the center. Time near a black hole. Time is a man made concept applying to earth's rotation towards the sun. If we were to watch something fall into a black hole we would see the thing slowing down after entering the Event Horizon until it would appear to stop near the singularity. But if we were the thing falling into the black hole we would experience it as going faster and faster and approaching the speed of light, at the same time the observers would see us slow down and when they see us "stop" we have actually reached the speed of light.
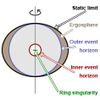
Some black holes spin arround an axis and that spinning creates a cosmic whirlpool. The outer bounderies of a spinning black hole are called a static limit, when you enter that part of the black hole you are forced to rotate with the black hole but you can still escape it. The Event Horizon is an imaginary sphere that astronomers use to measure how close to the center you can safely get (and return). The Event Horizon is composed of two spheres, the inner Event Horizon that surrounds the center, and the outer Event Horizon that lies within the Ergosphere (cosmic whirlpool) that surrounds the black hole. The Event Horizon has been translated as "the point of no return" because when a particle enters the Event Horizon it is impossible for it to return. The size of the Event Horizon is proportional to the mass of the black hole. "Astronomers have found black holes with event horizons ranging from 6 miles to the size of our solar system." (http://hubblesite.org/explore_astronomy/black_holes/encyc_mod3_q3.html)
Singularity is what you will find at the center of a black hole, it is where all the mass has been compressed into a region of zero volume. Inside the singularity "matter is crushed to an infinite density the pull of gravity is infinitely strong, and space/time has infinite curvature".(http://paradise7.hubpages.com/hub/The-Event-Horizon) This means that the mass of the black hole has become a point of zero volume and the gravitational pull is strong enaugh to power a whole galaxy. Some black holes at the center of galaxies have a mass as big as a billion of our sun and are called Supermassive black holes, and astronomers have discovered that there is a black hole at the center of most galaxies. Manny believe that there is a black hole at the center of all galaxies but that has yet to be put to the test.
The search for black holes. When astronomers look for black holes they cant really see anything, they are mostly looking for big suns that dissappear or things that seem to be orbiting arround a dot of notthing with very high gravity. In the search for black holes, seeing nothing in the telescope is a good sign. The only thing capable to escape a black hole's high gravity feald is radiation and as you reed this, scientists are measuring the radiation coming from places that might contain black holes.
Intervew: Marteinn Sęvarr, 23 year old University student studdying geology in HR, Iceland.
When I asked Marteinn why he was interested in black holes his answer didn't surprize me because it was the same reson I had for my interest in them. He said they were very complicated (mindfucking) and so hard to explain properly because they have to do with the third dimention, time. He first started studdying them by him self online after his physics class where his teacher told them about black holes and said he wasn't going to explain them to the class because they were just too complicated. Marteinn went home and looked them up on the internet and found a lot of articles trying to explain them but not very accuratly. It is very hard to find a good explanation for what a black hole is but he found Wikipedia and a few youtube videos very helpfull at explaining them. He found 3D pictures that show how stars bend the space arround them (similar to the photo I have here above) very helpfull and they really got him to understand the whole thing much better. As a result of his interest in black holes he started studdying the third dimention and his interest in astronomy and physics increased radically. The thing about black holes that amazes him the most is how much mass can be in such a tiny dot that it's as close to nothing as anything can be. Black holes brake every law of the physics world and we can't go in there to see what it is, it's just a big question mark and we are merely guessing in the gaps we can't get the facts for because there is no way for us to know what really happens inside a black hole.
Interesting documentaries on black holes are for example on Documentaryheaven.com under the search result of black hole. I recommend "Who's Afraid of a Big Black Hole", "Monster of the Milky Way" and "Supermassive Black Holes
References.
http://hubblesite.org/explore_astronomy/black_holes/encyc_mod3_q3.html
http://paradise7.hubpages.com/hub/The-Event-Horizon
Vocabulary:
Composed= put to gether from../ made from
Region= aeria/volume
Curvature= curving or bending.
region= aeria/length.
sufficiently= extremely (large).
thermodynamics= the branch of natural science concerned with heat and its relation to other forms of energy and work.
relativity= differences.
stellar= density.
interior= the inside.
friction= the rubbing together of two things.
extensively= very much.
pathological= unnaturally/abnormally.
continuum= anything that goes through a gradual transition from one condition, to a different condition, without any abrupt changes.
equivalent= a unit of amount of substance used in chemistry and the biological sciences.
dilution= the action of making something weaker in force, content, or value.
artificial= human made.
revolution (around the sun)= a rotation, to go around.
insufficient= not enough.
remnant= a part or quantity that is left after the greater part has been used, removed, or destroyed.
degeneracy= the state or quality of being degenerate.
Bloggar | 29.8.2012 | 10:23 (breytt 18.9.2012 kl. 18:25) | Slóš | Facebook | Athugasemdir (0)